The olfactory nerve is a fascinating topic to explore in the field of neuroscience. Understanding its anatomy, function, and disorders can provide valuable insights into the world of sensory perception. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the olfactory nerve and discuss effective writing techniques for scientific topics. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply curious about the olfactory nerve, this article will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to write about this complex subject matter.
Understanding the Olfactory Nerve
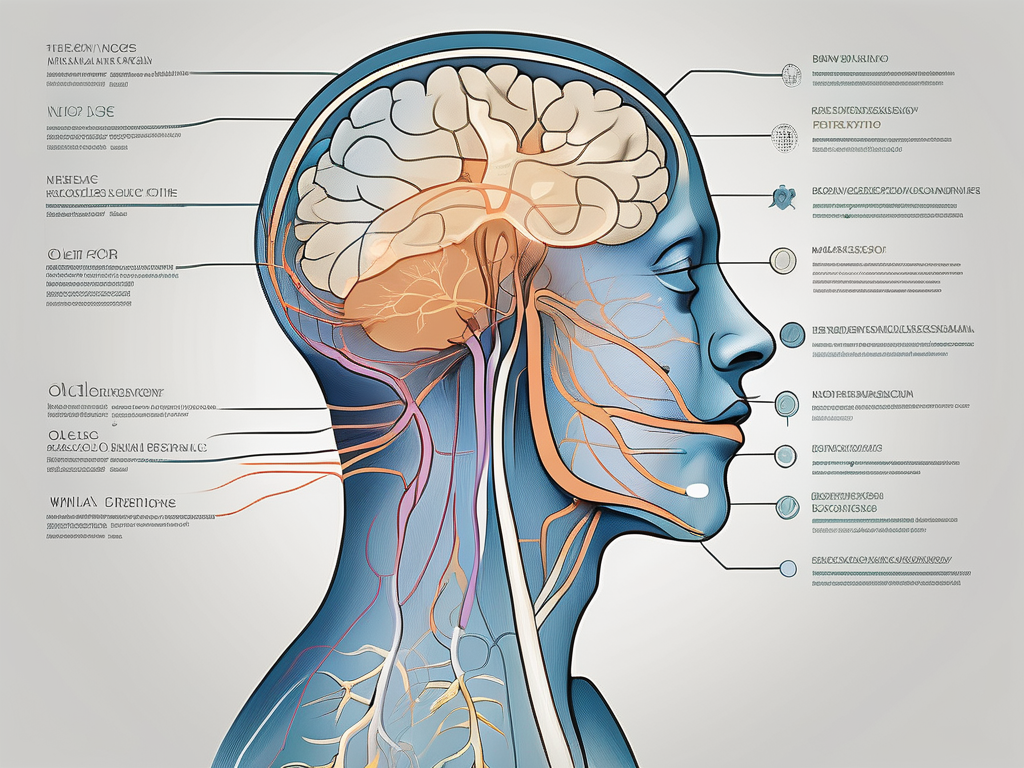
Before we begin exploring the olfactory nerve in detail, let’s first familiarize ourselves with what it is and its role in the human body. The olfactory nerve is the cranial nerve responsible for our sense of smell. It consists of specialized nerve cells, known as olfactory receptor neurons, which are located in the nasal cavity. These neurons detect odor molecules in the air and transmit signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive various scents.
Have you ever wondered why certain smells can evoke strong memories or emotions? Well, the olfactory nerve plays a significant role in this phenomenon. When we inhale a particular scent, the olfactory receptor neurons in our nasal cavity send signals to the brain’s limbic system, which is closely associated with memory and emotion. This connection explains why a whiff of a familiar fragrance can transport us back to a cherished moment or trigger a powerful emotional response.
The Anatomy of the Olfactory Nerve
To truly grasp the intricacies of the olfactory nerve, it is essential to understand its anatomical structure. The olfactory nerve originates from the olfactory epithelium, a specialized tissue located in the nasal cavity. From there, it extends through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone and enters the olfactory bulb, situated at the base of the brain. The olfactory bulb then connects to the olfactory cortex, forming a vital pathway for odor perception.
Interestingly, the olfactory epithelium is not a static structure. It undergoes continuous turnover throughout our lives. New olfactory receptor neurons are constantly being generated to replace old ones. This remarkable regenerative capacity allows our sense of smell to remain intact despite the wear and tear of daily life. However, in certain cases, such as severe nasal trauma or chronic sinusitis, this regenerative process may be disrupted, leading to a temporary or permanent loss of smell.
The Function of the Olfactory Nerve
The primary function of the olfactory nerve is to enable our sense of smell. When odor molecules bind to the olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity, they initiate a series of biochemical reactions that generate electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted along the olfactory nerve fibers to the olfactory bulb, where further processing occurs. From the olfactory bulb, the information is relayed to various regions of the brain, allowing us to identify and interpret different smells.
It is fascinating to note that the olfactory nerve is unique among the cranial nerves in its ability to regenerate throughout a person’s life. While other cranial nerves have limited regenerative capacity, the olfactory nerve can generate new receptor neurons to replace damaged ones. This remarkable regrowth potential holds promise for future therapeutic interventions, as researchers explore ways to harness the regenerative power of the olfactory nerve to treat various neurological conditions.
Disorders Related to the Olfactory Nerve
While the olfactory nerve is crucial for our sense of smell, it can be susceptible to certain disorders. Anosmia, the loss of the ability to smell, is one such condition that can greatly impact an individual’s quality of life. Other disorders, such as hyposmia (reduced sense of smell) and parosmia (distorted sense of smell), can also arise due to various factors, including trauma, infections, or neurological conditions. Understanding these disorders can help researchers and clinicians develop new treatment approaches and interventions.
Research into olfactory disorders is an active area of investigation, as scientists strive to unravel the underlying mechanisms and develop effective treatments. Recent studies have shown promising results in using gene therapy to restore olfactory function in animal models. These advancements bring hope for individuals suffering from olfactory disorders, offering the possibility of regaining their sense of smell and improving their overall quality of life.
The Role of the Olfactory Nerve in Sensory Perception
Our sense of smell is closely intertwined with other sensory modalities, such as taste and memory. By exploring the relationship between the olfactory nerve and these aspects of sensory perception, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexity of our senses.
The olfactory nerve, also known as the first cranial nerve or CN I, is a unique component of the nervous system that is responsible for our sense of smell. It is one of the twelve cranial nerves and is the only one that directly connects the brain to the outside environment. This direct pathway allows for the rapid transmission of olfactory information to the brain, where it is processed and integrated with other sensory inputs.
Olfactory Nerve and Smell
Smell and taste are two senses that are closely intertwined. The olfactory nerve plays a critical role in our ability to perceive certain flavors. It is responsible for detecting volatile compounds released by food and beverages, which then combine with taste receptors on the tongue to create a multisensory experience. This intricate relationship between the olfactory nerve and taste buds allows us to savor the diverse flavors found in our favorite dishes.
Furthermore, the olfactory nerve is capable of detecting a vast array of odors, ranging from pleasant fragrances to foul smells. This broad spectrum of olfactory stimuli contributes to the richness of our sensory experiences and can evoke powerful emotional responses.
Olfactory Nerve and Memory
The olfactory nerve has a unique association with memory that sets it apart from other sensory modalities. Certain scents have the power to evoke vivid memories and emotions, often referred to as the “Proust effect” after the famous French writer Marcel Proust. This phenomenon highlights the profound influence of the olfactory nerve on our emotional and autobiographical memory systems. Exploring the connection between smell and memory can unravel new avenues in cognitive research and therapy.
Studies have shown that the olfactory nerve is closely linked to the limbic system in the brain, which is responsible for processing emotions and memories. This close anatomical connection explains why certain smells can trigger intense emotional responses and transport us back in time to specific events or places. Understanding how the olfactory nerve interacts with the limbic system can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying memory formation and emotional regulation.
Writing Techniques for Scientific Topics
When writing about complex scientific topics like the olfactory nerve, it is crucial to employ effective writing techniques that convey information accurately and engage the reader. Let’s explore some strategies to simplify complex concepts, maintain scientific accuracy, and captivate your audience.
Simplifying Complex Concepts
Scientific topics can often be daunting for readers who are not well-versed in the subject matter. To make your writing accessible, strive to break down complex concepts into simpler terms and provide concise explanations. For example, when discussing the olfactory nerve, you could compare it to a telephone line that carries messages from the nose to the brain. This analogy helps readers grasp the function of the olfactory nerve in a relatable way.
Furthermore, incorporating visual aids such as diagrams or illustrations can also aid in simplifying complex concepts. These visual representations can provide a clear and concise overview of intricate scientific processes, making it easier for readers to understand.
Maintaining Scientific Accuracy
Precision and accuracy are fundamental when writing about scientific topics. Ensure that your information is up-to-date and supported by reliable sources. Cite references when necessary to reinforce the validity of your claims. For instance, when discussing the olfactory nerve, you could reference recent studies published in reputable scientific journals to support your statements.
Additionally, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations or uncertainties within the scientific field. Addressing potential counterarguments or alternative theories demonstrates your understanding of the subject matter and adds depth to your writing. By acknowledging different perspectives, you present a well-rounded and unbiased view of the scientific topic.
Engaging the Reader in Scientific Writing
Scientific writing does not have to be dry and monotonous. Engaging your audience is paramount to ensure they stay invested in the topic. Incorporate anecdotes, case studies, or real-life examples to make your writing relatable and captivating. For example, when discussing the olfactory nerve, you could share a story about how a particular scent triggered a vivid memory, highlighting the power of our sense of smell.
Furthermore, using a conversational yet professional tone can help strike a balance between scientific accuracy and reader-friendly language. Avoid excessive jargon and explain technical terms when necessary. By creating a friendly and approachable tone, you foster a connection with your readers, making them more likely to stay engaged throughout your writing.
Tips for Writing about the Olfactory Nerve
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of the olfactory nerve and the writing techniques needed for scientific topics, we will explore some additional tips specific to writing about this fascinating subject.
Delving deeper into the world of the olfactory nerve unveils a complex network of sensory neurons responsible for our sense of smell. This intricate system plays a crucial role in our daily experiences, from evoking memories to influencing our food preferences.
Researching the Olfactory Nerve
Before you embark on writing about the olfactory nerve, conduct thorough research to gather reliable and up-to-date information. Consult peer-reviewed articles, scientific journals, and reputable sources to ensure your content is accurate and credible. Additionally, consider interviewing experts in the field to gain further insights and perspectives.
Exploring the latest advancements in olfactory research can provide a fresh perspective on this sensory pathway. Understanding how the olfactory nerve interacts with the brain and contributes to our overall well-being can add depth and richness to your writing.
Structuring Your Writing
A well-structured article enhances readability and comprehension. Start with an informative introduction that provides an overview of the olfactory nerve and its significance. Subheadings can then help segment the content into distinct sections based on the various aspects you wish to discuss. Conclude your article by summarizing key points and inviting readers to explore further.
Unraveling the complexities of the olfactory nerve through a structured approach can guide readers on a journey through the science behind our sense of smell. By organizing your writing effectively, you can lead your audience through a seamless exploration of this intriguing topic.
Reviewing and Editing Your Work
Once you have written your article, take the time to review and edit your work. Proofread for grammar, spelling, and clarity of expression. Check that your content flows smoothly and is coherent throughout. Consider seeking input from colleagues or peers to gain valuable feedback and ensure your article is polished and error-free.
Editing your work with a critical eye can elevate the quality of your writing and ensure that your insights into the olfactory nerve are effectively communicated. By refining your content through meticulous editing, you can present a compelling narrative that captivates readers and deepens their understanding of this sensory marvel.
The Olfactory Nerve and the Vagus Nerve
While writing about the olfactory nerve, it is essential to address its relation to the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, plays a critical role in regulating various bodily functions, including digestion, heart rate, and breathing. Although both nerves have different functions, they can interact in certain situations, such as during the process of taste perception and the modulation of emotional responses. Further exploration of the olfactory nerve’s interaction with the vagus nerve can provide additional insights into the complexity of our sensory experiences.
It is fascinating to note that the olfactory nerve, responsible for our sense of smell, is unique among the cranial nerves as it is directly connected to the brain without passing through the thalamus. This direct connection allows for rapid processing of olfactory information and immediate responses to different scents. On the other hand, the vagus nerve, with its extensive reach throughout the body, acts as a communication highway between the brain and various organs, influencing a wide range of physiological processes.
As we delve deeper into the intricate relationship between the olfactory nerve and the vagus nerve, we uncover the interconnectedness of our sensory and autonomic nervous systems. The olfactory nerve not only plays a crucial role in detecting odors but also contributes to memory formation and emotional processing. In contrast, the vagus nerve’s involvement in the parasympathetic nervous system helps regulate rest and digest functions, highlighting the dynamic interplay between these two neural pathways.
As we conclude this article, we hope that you now feel equipped to write about the olfactory nerve with confidence and expertise. Remember to approach the topic with accurate information, engage your audience, and craft your writing in a manner that conveys your knowledge and passion for the subject. Happy writing!







Leave a Reply